Spina Bifida is basically a part of a group of birth defects which are known as neural tube defects. The neural tube is an embryonic structure which will eventually develop into the brain of a baby along with spinal cord & tissues which enclose them. Neural tubes are normally formed early during pregnancy & generally close by the 28th day following conception. However, in babies with spina bifida, a portion of this neural tube fails to close or develop properly. This goes on further to cause a defect in the development of the spinal cord & within the bones of the spine. Moreover, spina bifida is found to occur in varying forms of severity. Treatments for spina bifida are surgically performed when required, even though such treatments do not always completely resolve the issue.
Signs & Symptoms of Spina Bifida
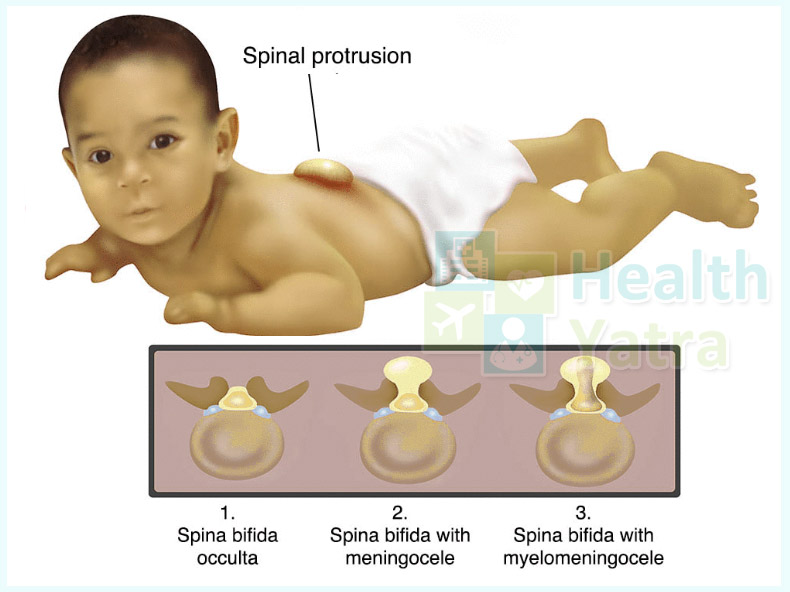
Spina bifida is generally found to occur in 3 forms, where each is varying in severity.
- Spina Bifida Occulta – This is the mildest form of spina bifida resulting in a gap or separation in one or more bones (vertebrae) of the spinal column. However, most children suffering from this form of spina bifida display no signs or symptoms & also do not experience any neurological problems because the spinal nerves are not involved in this condition. Visible indications of spina bifida occulta can, however, sometimes be seen on the skin above spinal defect in babies, including the following.
- Simple birthmark or dimple
- Collection of fat
- Abnormal tuft of hair
Many people having spina bifida occulta do not even know that they do unless this condition is discovered during an X-ray procedure or from other imaging tests performed for unrelated reasons.
- Meningocele – This is a rare form of spina bifida where meninges or membrane around the spinal cord pushes out through the openings in the vertebrae. These membranes can be effectively removed through surgery with little or no damage to the nerve pathways because the spinal cord is capable of developing normally.
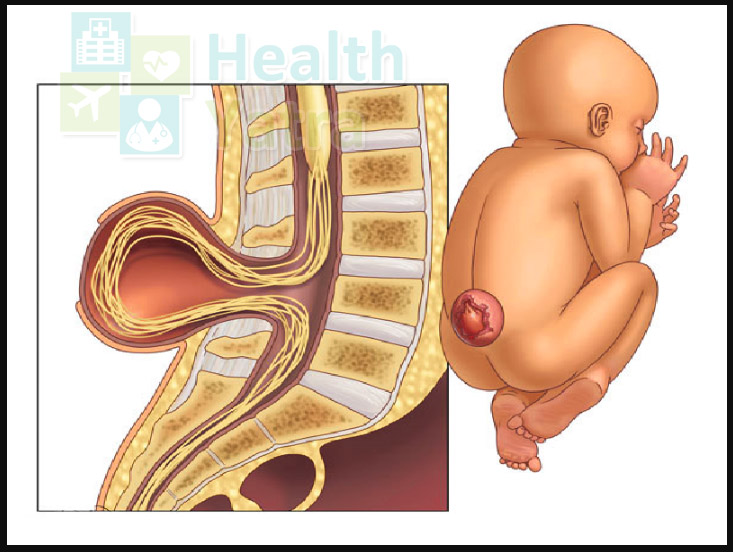
- Myelomeningocele – Also called open spina bifida, myelomeningocele is the most severe form & usually the one when people use the term “spina bifida”. Spinal canal of babies remain open along several vertebrae in the middle or lower back in cases of myelomeningocele. Due to this kind of an opening, both the spinal cord & membranes protrude at birth & form a sac on the back of babies. However, in some cases, skin is found to cover the sac. Usually, nerves & tissues are exposed & which make the baby more prone to life-threatening infections. Neurological impairment is also common, including the following.
- Seizures, especially when the child is requiring a shunt
- Bladder & bowel problems
- Weakness in muscles of legs & which sometimes involve paralysis
- Orthopedic problems like uneven hips, deformed feet & scoliosis (spinal curvature)
Causes of Spina Bifida
Doctors are still not certain as to what causes spina bifida. Like it is with many other healthcare problems, spina bifida also appears to result from a combination of genetic & environmental risk factors including folic acid deficiency & family history of neural tube defects.
Risk Factors Associated with Spina Bifida
Although researchers & doctors do not know for sure as to what causes spina bifida, a few risk factors including the following have been identified by them.
- Race – Cases of spina bifida are found to be more common among whites & Hispanic populations.
- Sex – Girls are found to be more affected by spina bifida.
- Family History of Neural Tube Defects – Couples who already have one child with neural tube defect have a slightly higher chance of having another child with the same defect in future. This risk increases further when two children have previously been affected with this condition. Additionally, women born with neural tube defects or having a close relative with this condition, have a greater chance of giving birth to children with spina bifida. Nevertheless, most babies with spina bifida are born to parents having no known family history of this condition.
- Folate Deficiency – Folate or Vitamin B-9 is very important for the healthy development of babies. Folate, in fact, is the natural form of this vitamin. The synthetic form which is usually found in fortified foods & supplements is called folic acid. Deficiency of folate is found to increase the risk of spina bifida & other neural tube defects.
- Certain Medications – Anti-seizure medicines like valproic acid (Depakene) are found to cause neural tube defects when they are taken during pregnancy. This is because they can interfere with the ability of the body to utilize folate & folic acid.
- Diabetes – When women with diabetes do not properly control their blood sugar, they are found to have a higher risk of having babies with spina bifida.
- Obesity – Pre-pregnancy obesity is generally associated with increased risk of having babies with neural tube birth defects, including spina bifida.
- Increased Body Temperature – There is some evidence to suggest that hyperthermia or increased body temperature during early weeks of pregnancy might increase the risk of having babies with spina bifida. Use of hot tubs, saunas, or fever can elevate the core body temperature of pregnant mothers & which has been associated with having increased risk of delivering babies with spina bifida.
Women having known risk factors for spina bifida must, therefore, talk to doctors in order to determine whether they need large doses or prescription doses of folic acid, even before the start of pregnancy. Women taking medications should also let their doctors know. In case plans are made ahead of time, some of these medications can either be adjusted or even stopped in order to diminish potential risk of having babies with spina bifida.
Complications Associated with Spina Bifida
Most often spina bifida may cause no symptoms but only some minor physical difficulties. However, it may frequently lead to severe mental & physical disabilities in future.
Factors Affecting Severity in Spina Bifida
The severity of spina bifida is affected by the following:
- Location & size of neural tube defect
- Whether skin is covering the affected area
- Type of spinal nerves which are coming out of the affected area of spinal cord
Range of Complications
Complications generally include the following:
- Physical & Neurological Problems – These problems generally include lack of normal bladder & bowel control & partial or complete paralysis of legs. Both children & adults with this form of spina bifida may need braces, crutches or wheelchairs so as to help them get around. However, these conditions usually depend upon the size of the opening in spine & the care patients receive after birth.
- Hydrocephalus – Accumulation of Fluid in Brain – Children born with myelomeningocele are also found to commonly experience accumulation of fluid within the brain. This condition is medically known as hydrocephalus. Most babies born with myelomeningocele will, however, require a ventricular shunt procedure. This surgical intervention allows a surgical placement of tube which allows the accumulated fluid inside the brain to drain into the abdomen when needed. This tube is generally placed soon after birth during the surgical procedure to close the protruding sac on the lower back or sometime later on the accumulation of fluid.
- Meningitis – Infection in Tissues Surrounding Brain – Quite a few babies born with myelomeningocele are found to develop meningitis. Meningitis is an infection affecting the tissues which surround the brain & may also sometimes cause brain injury which can be life-threatening.
- Other Complications – Additional problems may also arise for children with spina bifida as they get older. Children affected with myelomeningocele can also develop learning disabilities like difficulty in paying attention, problems associated with language, reading & comprehension along with trouble learning mathematics. Some children with spina bifida are also found to experience problems with skin, latex allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, urinary tract infections & depression.
Preparing for Initial Appointment for Spina Bifida
Healthcare providers are most likely to diagnose or suspect the baby’s spina bifida condition during the pregnancy itself. Following this pregnant mothers are also most likely to consult a multidisciplinary team comprising of physicians, surgeons & physical therapists at a center specializing in spina bifida treatment of their choice. However, since these appointments with specialists can be brief & there is a lot to discuss, it would be a sensible idea for expecting mothers to be well prepared for the initial appointment. Following is a list of some helpful information which can empower expecting mothers to get ready & stay informed as to what to expect from the healthcare providers in case there are suspicions that the baby may be having spina bifida.
What Expecting Mothers Can Do
- Be Aware of Pre-Appointment Instructions – Expecting mothers should make sure to ask if there is anything they are required to do in advance at the time when they seek an appointment. These pre-appointment instructions can include instructions like drinking extra water before an ultrasound.
- Making a List of Medication – A complete list would include medicines, vitamins & supplements which the expecting mother has taken before & during pregnancy.
- Bring Along a Friend or Family Member for Initial Consultation – Quite often it can be difficult for the expecting mother to remember all information which was provided to them during the initial consultation. Someone accompanying them can help remember if there was something they have missed or forgotten.
- Writing Down Questions to Ask Doctors – Preparing a list of questions before hand can help make the most of the time which is available with the healthcare provider. This list can include questions from the most important to the least important in case time is running out. Following is a list of some basic questions relating to spina bifida which expecting mothers can ask doctors.
- Is my baby having spina bifida & how severe is it?
- Is there any evidence of water in my baby’s brain (hydrocephalus)?
- Is it possible to treat the baby during pregnancy?
- What can be done for my baby soon after birth?
- Will treatments for spina bifida cure my child?
- Will treatments have lasting effects?
- Where can I contact to know about community resources which may prove helpful for my child?
- What odds are there of spina bifida happening again in future pregnancies?
- Can you provide me with brochures & other printed material regarding spina bifida?
- Which websites do you recommend I visit to know more about spina bifida?
What to Expect From Doctors During Initial Appointment
Doctors are most likely to ask a number of questions to expecting mothers. Staying prepared to answer them will reserve time to discuss other points which expecting mothers may want to ask. Nevertheless, following are the most common questions doctors ask during initial appointment screening for spina bifida.
- Did you ever have children with spina bifida or any other birth defects?
- Are you having any family history of spina bifida?
- Are you presently taking any anti-seizure medications or were you taking them at the start of pregnancy?
- Are you aware of resources which are available in your community meant to support you & the child in dealing with spina bifida?
- Are you able to travel to facilities which offer specialized care for spina bifida?
Tests & Diagnosis for Spina Bifida
Expecting mothers are normally offered prenatal screening tests in order to check for spina bifida & many other birth defects. However, these tests are generally not perfect. Many times, mothers whose blood tests have come positive are found to have normal babies. Moreover, even in cases where blood results are negative, there still remains a small chance that spina bifida is present. Expecting mothers should, therefore, talk to their doctors about prenatal testing procedures, associated risks, & how to handle them.
- Blood Tests – Doctors are most likely to check for spina bifida by performing the following tests:
- MSAFP or Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Test – MSAFP is a common test which is utilized to check for myelomeningocele. For this purpose, doctors will draw a blood sample & send it to a laboratory. The lab will subsequently test it for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), which is a protein produced by babies. However, it is quite normal for small amounts of AFP to cross the placenta & enter the blood stream of mothers to be. But abnormal high levels of AFP suggest that the baby is having a neural tube defect which can most commonly be anencephaly or spina bifida. This is a condition characterized by a brain which is underdeveloped & an incomplete skull. Some cases of spina bifida, however, do not produce high levels of AFP. On the flip side, even when high levels of AFP are found, neural tube defects are present only in a small percentage of babies. Varying levels of AFP can also be caused by other factors. These include multiple babies or miscalculation in the age of the fetus. For this reason, doctors may often order a follow-up blood test for confirmation. In case results are still high, expecting mothers would require further evaluation, including ultrasound examination.
- Other Blood Tests – Doctors often perform MSAFP test along with 2 – 3 other blood tests which may detect hormones like estriol, inhibin A & human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). This combination is called a triple screen or quad screen (quadruple screen) depending upon the number of tests. Moreover, these tests are normally performed with MSAFP, but their objective, however, is to screen for Down syndrome (trisomy 21) & not neural tube defects.
- Ultrasound – Obstetricians generally rely on ultrasonography for the screening of spina bifida. When blood tests have indicated high levels of AFP, doctors would suggest an ultrasound examination in order to help determine reasons behind it. Most common ultrasound examinations bounce high-frequency sound waves of the tissues in the body so as to format black & white images on a video monitor. Information provided through these images help establish whether there are one or more than one babies & also help confirm the gestational age. Both these factors are found to affect AFP levels. Moreover, advanced ultrasound can also help detect signs of spina bifida, like if the baby is having an open spine or displaying particular features in the baby’s brain indicating spina bifida. Ultrasound nowadays in expert hands is very effective in detecting spina bifida & for assessing its severity. Ultrasound is also safe for both the baby & the mother.
- Amniocentesis – Doctors may usually offer amniocentesis when blood tests show high levels of AFP in blood but ultrasound proves to be normal. Doctors generally use a needle to remove a sample of fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding the baby during amniocentesis procedure. Analysis conducted on samples will indicate levels of AFP which is present in amniotic fluid. However, a small amount of AFP is normally found within amniotic fluid. But then, amniotic fluid contains an elevated amount of AFP whenever an open neural tube defect is present because of the fact that skin surrounding the baby’s spine is absent & therefore AFP eventually leaks into the amniotic sac. Expecting mothers should, however, discuss risks of this test with doctors, including a slight risk of pregnancy loss.
Spina Bifida Treatment in India & Drugs for
Treatments for spina bifida usually depend upon the severity of the condition. Moreover, spina bifida occulta mostly does not require any treatment at all, but other types of spina bifida do require a range of treatments.
- Surgery – Meningocele usually involves surgical intervention in order to put meninges back into place & for closing the openings in vertebrae. Myelomeningocele cases also require surgery & usually within 24 – 48 hours following birth. Early performance of surgery can effectively minimize the risk of infection which is generally associated with exposed nerves. This will also help in protecting the spinal cord from undergoing any other additional trauma. Neurosurgeons during this procedure will place the spinal cord & exposed tissue within the body of the baby & cover them with muscles & skin. In some cases, a shunt is also placed within the baby’s brain along with the operation on the spinal cord, in order to control hydrocephalus.
- Prenatal Surgery – During this procedure, which is usually performed prior to the 26th week of pregnancy, surgeons with help of a surgical intervention, expose the uterus of a pregnant mother. Subsequently, they will open the uterus & repair defective spinal cord of the baby. However, proponents of fetal surgery believe that functioning of nerves in babies with spina bifida appears to rapidly worsen the following birth. Therefore it may be better to repair defects pertaining to spina bifida while mothers are still pregnant & the baby is still developing within the uterus (In-Utero). So far, it is found that children who have undergone fetal surgery needed fewer shunts & are also less likely to require crutches or other walking devices. However, this operation along with the baby also poses risks to the mother & greatly enhances the risk of premature deliveries. Pregnant mothers should, therefore, discuss with doctors whether this is the right procedure for them.
- Ongoing Care – Treatment for spina bifida does not end with the initial surgery. Irreparable nerve damage is already done in babies born with myelomeningocele & ongoing care involving a multidisciplinary team of physicians, surgeons & therapists is most often required. Moreover, babies with myelomeningocele will also require further operations for many associated complications. Bladder & bowel problems along with paralysis often remain & treatment for these conditions, typically start immediately following birth. Babies born with myelomeningocele may also have to start with exercises which are meant to prepare their legs for walking with help of crutches or braces as they grow older. Many of these spina bifida cases also have a tethered spinal cord. This is a condition where the spinal cord is bound to the scar of closure & is, therefore, less able to properly grow in length along with the growth of the child. This ‘tethering’ process is also progressive & can cause loss of muscle function to the bladder, bowel or legs. However, surgery can often limit the degree of disability & which may also restore some function.
- Cesarean Birth – Birth through cesarean can be a strategic part of treatment for spina bifida as many babies with myelomeningocele often tend to be in breech (feet-first) position. A cesarean birth may be a safer & ideal method to deliver the baby when they are in a breech position or when doctors have detected a large cyst.
Coping & Support for Spina Bifida
News of the newborn child having a condition like spina bifida can naturally cause fear, frustration, anger, grief & sadness to parents. However, there is a good reason for hope as most people with spina bifida, in fact, live active, productive & full lives, especially when support & encouragement is received from loved ones. Most children, even with severe spina bifida, can walk for short distances with the assistance of canes, crutches or braces, but for longer distances they would invariably require wheelchairs. Nevertheless, using such devices can help children compensate for their condition alongside gaining more independence. Several children with spina bifida are found to have normal intelligence, provided they are given early educational intervention in order to deal with initial learning problems. Moreover, they may also require extra help from counselors & teachers to adapt with schooling. Since physical disabilities like spina bifida can also often cause emotional & social problems, these children require encouragement to participate in activities with peers & to lead independent lives within their capabilities & limitations. It may, therefore, be helpful to remember that they have no idea as to what is accepted as normal function & may therefore often adapt to their conditions in remarkable ways. Parents of children with spina bifida can also benefit from finding support groups or some other parents who are dealing with this condition. Talking to others who can understand the challenges & rewards of living with spina bifida can be extremely beneficial.
Preventive Measures for Spina Bifida
Women should take folic acid in supplement form & should start the course at least one month prior to conception & continue this through the first trimester of pregnancy. This will greatly reduce the risk of developing spina bifida & various other neural tube defects.
- Get Folic Acid First – It is critical for pregnant mothers to have enough folic acid within their system during the early weeks of pregnancy in order to prevent cases of spina bifida. Since many women are unable to discover when they get pregnant until this time, experts recommend all women of childbearing age should take a supplement of 400 mcg (micrograms) of folic acid every day. Moreover, several foods like rice, pasta, bread & breakfast cereals are fortified with the required dosage of folic acid per serving. Folic acid is generally listed on food packaging as folate & which is the natural version commonly found in food items.
- Planning Pregnancy – Experts suggest that supplementation of at least 400 mcg of folic acid everyday is the best approach for women who are actively trying to conceive as part of a planned pregnancy. It is found that the human body does not absorb folate as easily as it can absorb the synthetic folic acid. Most people are unable to get the recommended amount through diet alone. In such circumstances, vitamin supplements of folic acid are necessary for preventing cases of spina bifida. Moreover, folic acid is also found to help reduce the risk of other birth defects like cleft palate, cleft lip & some other congenital heart defects. However, it is a good idea to eat a healthy diet which includes foods which are enriched with folic acid or are rich in folate. This vitamin is naturally present in many foods including the following.
- Beans
- Dark green vegetables like spinach & broccoli
- Egg yolks
- Citrus fruits & juices
- When Higher Doses of Folic Acid are Required – People having spina bifida or mothers who have previously given birth to children having spina bifida will require extra folic acid before they plan to get pregnant. Women having diabetes or taking anti-seizure medications may also benefit from this higher dose of vitamin B. Recommended dose of folic acid in such cases may go up to 4 mg (4,000 mcg) which should begin one month prior to conception & definitely during the first few months of pregnancy. It would, however, be sensible to check with doctors before starting an additional folic acid supplement program.
Affordable Spina Bifida Treatment in India
India has emerged as a leading global medical tourism destination over the past few decades. Apart from the low-cost advantage, healthcare procedures in India are of high quality. With success rates at par with the best in the world, there is so many international patients from all around the world can gain without compromising anything. Many of the large pool of doctors & surgeons in the country have initially trained & experienced in developed western countries before returning to their homeland. Featuring an extensive network of healthcare services, most hospital facilities in India are either nationally or internationally accredited in order to adhere to excellent standards. These healthcare facilities are also equipped with the latest technologies & managed by well trained English speaking nurses & professional staff so as to make the international guests feel comfortable.
Avail Low-Cost Surgery for Spina Bifida with HealthYatra
In sync with the developing Indian healthcare success story, HealthYatra has established itself as the leading medical tourism platform offering affordable medical procedures to the international patient. Associated with top doctors & surgeons & the best hospital facilities in the country, HealthYatra is well poised to pass on a number of benefits to international patients. Whole range of seamless healthcare services provided by HealthYatra, in fact, begins with the first telephonic conversation with the patient & moves on to identifying the best doctor & ideal hospital for treatment. Other important streams of essential services include assisting the patient & his/her accomplice obtain medical visas, warm reception at airport when patients arrive for treatments, convenient modes of local travel, comfortable accommodation options which include budget or luxury hotels or serviced apartments near the treatment facility, scheduled appointments with doctors & surgeons for diagnosis & treatments without any waiting periods, choice of an exotic recuperative holiday at reasonable costs, follow-up evaluation checks & a successful farewell when the patient is finally heading back home.