Definition
Sperm passes from the testes to the penis in tubes called the vas deferens. A vasectomy is a surgery that blocks these tubes. This makes a man unable to make a woman pregnant.
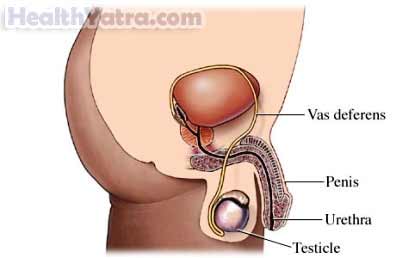
Reasons for Procedure
The surgery is done to make you sterile. This means that you are unable to cause a pregnancy.
A vasectomy is done as permanent birth control. This option is for men who are sure they will not want to father a child in the future. There is a surgery to reverse a vasectomy. However, the reverse is not always successful.
Possible Complications
If you are planning to have a vasectomy, your doctor will review a list of possible complications with you, which may include:
- Infection
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Chronic pain in and around the testes
- Sperm granuloma (lumps due to immune system response to sperm leaking from the reproductive organs)
- Ability to still make a woman pregnant
Factors that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Smoking
- Local infections
- Bleeding disorders
- Prior surgery in that area
What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
Your doctor may do the following:
- Physical exam
- Medical history
- Review of medicines
- Discuss the effects of this procedure
Talk to your doctor about your medicines. You may be asked to stop taking some medicines up to one week before the procedure. These include:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plavix) or warfarin (Coumadin)
In the days leading up to your procedure:
- Arrange for a ride to and from the procedure.
- Wear comfortable clothing.
- Take any medicine as ordered by your doctor. A mild sedative before the procedure may be recommended.
- Shower before leaving home.
- You may be asked to clip your scrotal hair.
Anesthesia
Local anesthesia will be used. It will numb the area. You may also be given medication to help you relax.
Description of the Procedure
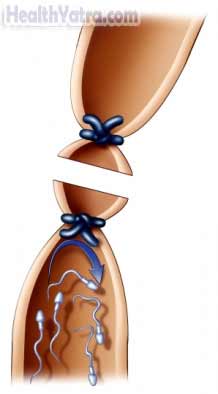
There are three techniques for a vasectomy:
- Conventional approach—One small cut will be made in the skin on each side of the scrotum. The vas deferens will be pulled through the openings. The tubes will then be cut. A small piece of the tubes may also be removed. The ends of the tube will be sealed off with stitches, clips, or an electrical pulse. The vas deferens will then be placed back into the scrotum. The incision will be closed with stitches.
- No-scalpel vasectomy—The doctor will locate the vas deferens under the scrotal skin. A clamp will be attached to hold it in place. A special tool will be used to punch a small hole in the skin. The hole will be stretched open to pull the vas deferens through. The tubes will then be cut and sealed as above. The holes will heal without stitches.
- Vas clip vasectomy—The vas deferens will be exposed in either of the two manners above. Special clips will be placed around each vas deferens and cinched in place. The clips will block the flow of sperm beyond the position of the clip.
How Long Will It Take?
Conventional vasectomies take about 30 minutes. No-scalpel procedures take about 20 minutes.
Will It Hurt?
Anesthesia prevents pain during the procedure. You can expect some soreness for a few days. Take pain medicines as directed by your doctor.
Post-procedure Care
When you return home, do the following to help ensure a smooth recovery:
- Apply ice packs, covered with a towel, on and off during the first eight hours.
- Ask your doctor about when it is safe to shower, bathe, or soak in water.
- Wear an athletic supporter if recommended by your doctor.
- Keep the area clean and dry.
- Cover the incisions with clean gauze for three days, or as directed by your doctor.
- A small amount of blood on the gauze pads is normal. Tell your doctor if you have excessive bleeding or need to change the gauze pads more than 2-3 times daily.
- Your doctor may give you antibiotics for several days following the procedure. Take all medicines as instructed.
- Do not lift heavy objects or participate in sports for 2-3 weeks.
- Be sure to follow your doctor’s instructions.
Most men feel fine to go back to work in a few days. They may also feel ready for sexual activity in about a week. Ejaculation may cause some discomfort in the groin and testicles until the tissues heal.
A vasectomy may not make you sterile right away. Tests will be done to look for any sperm in the semen. The tests may be done at your doctor’s office or with a home test kit. These tests are done to make sure that the procedure was effective.
You will need to use another form of birth control until the tests show there is no sperm in your semen.
Although a vasectomy is very effective, it is not a 100% guarantee that you will never be able to make a woman pregnant.
Call Your Doctor
After arriving home, contact your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Redness, swelling, increasing pain, excessive bleeding, or discharge from the incision site
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain that you cannot control with the medicines you have been given
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.
