Definition
This is surgery to repair a damaged or torn tendon.
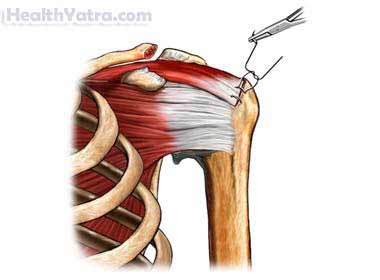
Reasons for Procedure
A tendon attaches muscle to bone. If a tendon tears, the muscle will no longer be able to work properly. This will cause weakness. Reattaching the tendon can fix the weakness.
Possible Complications
Problems from the procedure are rare, but all procedures have some risk. Your doctor will review potention problems like:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Formation of scar tissue that interferes with normal tendon movement
- Partial loss of function in the involved joint
If your age is 60 years or older, it may increase risk of complications. Other factors include:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Poor overall health
- Use of certain medications
What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
Your doctor will perform a physical exam. You may also need some tests. These may include:
- Blood test
- Urine test
- Ultrasound
- MRI
Leading up to the procedure:
- Talk to your doctor about your medications. You may need to stop taking some medications 7 days prior to your procedure. These may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Blood thinners
- Anti-platelet drugs
- Arrange for a ride home from the care center.
- The night before, eat a light meal. Do not eat or drink anything after midnight.
Anesthesia
Depending on where the tendon is located, you may be given:
- General anesthesia—you will be asleep during the procedure
- Regional anesthesia—to numb specific region of the body
- Local anesthesia—to numb the surgical site
Description of the Procedure
The doctor will make a cut in the skin over the injured tendon. The torn ends of the tendon will be sewn together or reattached to the bone. If you have a severe injury, a tendon graft may be needed. In this case, a piece of healthy tendon will be taken from another part of the body. This healthy tendon will be used to reconnect the broken tendon. The doctor will examine the area for injuries to nerves and blood vessels. Lastly, the incision will be closed with stitches.
Immediately After Procedure
The doctor may put you in a splint or cast. This is to keep the injured area in position for proper healing. The splint or cast will usually stay on for a period of weeks.
How Long Will It Take?
This depends on where the tendon is located and the severity of the injury.
Will It Hurt?
Anesthesia will keep you pain-free and comfortable during the procedure. To reduce pain after the procedure, your doctor may recommend pain medication.
Post-procedure Care
At the Care Center
After the procedure, you will be in a recovery room. The staff will monitor your progress. You may also get pain medication.
At Home
When you return home, take these steps:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions on cleaning the incision site.
- Ask your doctor about when it is safe to shower, bathe, or soak in water.
- Your doctor or physical therapist will recommend exercises or rehabilitation program.
- Be sure to follow your doctor’s instructions.
Follow these guidelines to care for your splint or cast:
- If you have a cast, do not get it wet. When you are cleared by your doctor, cover the cast with plastic when you bathe. If you have a fiberglass cast and it gets wet, you may dry it with a hair dryer.
- Bathe or shower as usual after the splint or cast is removed.
Call Your Doctor
Call your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Redness, swelling, increasing pain, excessive bleeding, or discharge from the incision site
- Pain that you cannot control with the medicines you have been given
- Your cast or splint becomes wet, dirty, or broken
- Skin below the cast becomes cold, discolored, numb, or tingly
- Cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, or severe nausea or vomiting
- New or worsening symptoms
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.
