Definition
This is an imaging test that uses a special contrast material to view the spinal cord. Along with an x-ray, the contrast material can help your doctor clearly outline the space containing the spinal cord and nerves. An x-ray is a test that uses radiation to take a picture of structures inside the body.
Reasons for Procedure
This is used to detect problems in and around the spinal cord, such as:
- Spinal tumors
- Herniated disks
- Narrowing of the spinal canal
Possible Complications
Complications are rare, but no procedure is completely free of risk. If you are planning to have myelography, your doctor will review a list of possible complications, which may include:
- Headache
- Allergic reaction to the contrast
- Bleeding
- Inflamed or infected spinal cord
What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
Your doctor may do the following:
- Physical exam and medical history
- Ask if you are pregnant—this test is not usually done on women who are pregnant
- Discuss your medicines with you, as you may need to stop or change the dosing
- Determine if you have any allergies
- Possibly prescribe a mild sedative to help you relax
Leading up to your procedure:
- The night before, do not eat solid foods after midnight. You should continue to drink liquids.
- If your doctor prescribes a sedative:
- Arrange to have someone drive you home. Also, arrange for someone to help you at home.
- Take the sedative before the exam as directed by your doctor.
Anesthesia
There is usually no anesthesia with this procedure. Your doctor may give you a mild sedative. You may have local anesthetic to reduce the pain of the needle.
Description of the Procedure
You will lie on your side or face down. Or, you may sit on the edge of a table, leaning forward. You may be given a local anesthetic injection in your back.
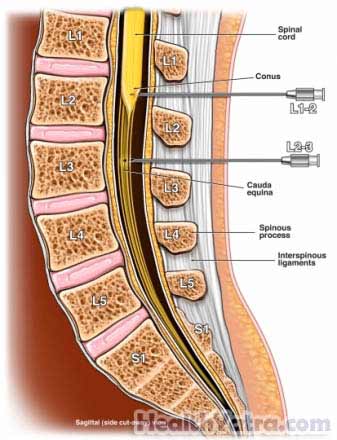
Your doctor will insert a needle into the space between your vertebrae. A small amount of fluid will be removed from the spinal canal. Next, the contrast will be injected through the needle. Your doctor will use an imaging procedure called fluoroscopy. This combines an x-ray unit with a camera and a screen.
To take the images, you will be positioned stomach-down on the table. A brace will be against your shoulders. The table will be tipped forward. Next, the doctor will take images of your back. You will hold your breath while the images are taken. You may be asked to turn slightly to one side and then the other.
Often, your doctor will perform a CT scan after myelography. This is to see the spread of the contrast dye.
Immediately After Procedure
You may be asked to stay in the exam room while the doctor looks at the images. You will be able to go home after about an hour.
How Long Will It Take?
About 30-60 minutes (CT scan will take 30-60 minutes longer)
How Much Will It Hurt?
You will have some pressure or pain when the needle is inserted.
Post-procedure Care
- If you took a sedative, do not drive, operate machinery, or make important decisions until the sedative wears off.
- Avoid strenuous exercise (including bending over) for 1-2 days.
Call Your Doctor
After you leave the hospital, contact your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Headache lasting more than 24 hours
- Excessive nausea or vomiting
- Neck stiffness
- Numbness in your legs
- Trouble urinating or moving your bowels
- Symptoms of allergic reaction (eg, hives, itching, nausea, swollen or itchy eyes, tight throat, difficulty breathing)
- Worsening of your symptoms
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.
