Definition
Liposuction is an elective surgical procedure. It reshapes the body through the removal of excess body fat.
Reasons for Procedure
Some common reasons for choosing to have liposuction include:
- Reshaping the body so that it is more in tune with an individual’s ideal body image
- Removing unwanted fat pockets that could not be lost with diet and exercise
- Boosting self-confidence and feelings about appearance
- Reducing the chest size of males suffering from gynecomastia (enlarged breasts)
- Removing fatty deposits known as lipomas
Possible Complications
Complications are rare, but no procedure is completely free of risk. If you are planning to have liposuction, your doctor will review a list of possible complications, which may include:
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Allergic reaction
- Burns
- Asymmetry
- Darkening of the skin
- Irregular appearance of the area
- Firm scarring under the skin
- Fluid build up under the skin
Liposuction results are not the same for everyone. Some factors that may affect results include:
- Age—Older patients may not see the same results as younger patients, because their skin is less elastic.
- Experience of the doctor—Doctors with more experience tend to have fewer problems.
Some factors that may increase the risk of complications include:
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Severe heart or lung disease
- Taking certain medicines
- Poor blood circulation
- Recent surgery in the area to be suctioned
- Prior liposuction in the area to be suctioned
- Having a large area suctioned or large amounts of fat removed
What to Expect
Prior to Procedure
Your doctor will likely:
- Evaluate you as a candidate for liposuction:
- Ask about your medical history, illnesses, medicines, drug allergies, and previous surgeries
- You may be asked to stop taking some medicines (including herbal supplements) up to one week before the procedure, like:
- Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs
- Blood thinners, such as clopidogrel (Plavix) or warfarin (Coumadin)
- Discuss previous weight losses/gains and how they affected your body
- Have you identify the areas you would like to have suctioned
- Test your skin’s elasticity (ability of the skin to stretch and return to normal)
- Estimate the amount of fat needed to be removed for best results
- Discuss your ideal surgical outcome and body image versus realistic expectations
- Determine your emotional stability (After surgery, some patients tend to become temporarily depressed.)
- Discuss the different types of liposuction available
- Prepare you for the procedure by:
- Discussing surgical techniques and anesthesia options
- Determining if the procedure should be conducted in a surgical center, at an outpatient clinic, or in a hospital—The location will depend on the amount of fat to be removed. When large amounts of fat are removed, it is safest to do the surgery in a hospital.
- Giving you instructions
- Addressing your questions and concerns
Leading up to your procedure:
- Refrain from smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding diet.
- Arrange for a ride and for help at home.
- The night before, eat a light meal. Do not eat or drink anything after midnight.
- If advised by your doctor, take a shower in the morning or the night before the procedure. You may need to use special antibacterial soap.
Anesthesia
There are two anesthesia options for liposuction. Your doctor will help you to decide which is best for you.
- Local anesthesia—This numbs the area. You will be awake during the procedure.
- General anesthesia —You will be asleep during the procedure.
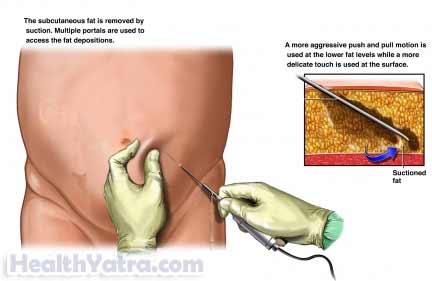
Description of Procedure
A special fluid containing saline (salt water), additional anesthetic, adrenalin (to minimize bleeding), and bicarbonate (to minimize pain from injection) will be injected into the fatty areas. You may have an incision for the fluid injection. One of the following three extraction techniques will be used:
- Wet technique—The amount of fluid injected is less than the amount of fat to be removed.
- Super wet technique—The amount of fluid injected is equal to the amount of fat removed.
- Tumescent technique—Two or three times as much fluid is injected into the body as fat removed.
After the fluid is added, a small incision will be made near the area to be suctioned. In traditional liposuction, the doctor will use an instrument called a cannula to suction the fat. A cannula is a hollow tube, like a drinking straw. A vacuum pressure unit, which is attached by a hose to the cannula, will provide the suction for the procedure. Once fat has been removed, the incisions may be sutured closed or left open to drain.
The following are different types of liposuction available:
- Power-assisted liposuction—This involves the used of a vibrating cannula that disrupts the fat cells prior to their removal. The technique is especially useful in areas where the fat is more difficult to remove or in areas previously liposuctioned.
- Ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty (UAL)—This involves the use of ultrasound energy provided via a probe under the skin. The fat cells are disrupted and the fat is then removed by traditional liposuction. There may be a reduction in bleeding and swelling and an increase in skin tightening with this procedure.
- Laser-assisted lipolysis—This involves the use of a laser fiber placed under the skin. Heat is used to liquefy fat prior to removal by traditional liposuction. The laser coagulates blood vessels to minimize bleeding and swelling, and it also causes the skin to tighten.
- Water-assisted liposuction—This involves the use of a special cannula that sprays water to gently disrupt fat cells prior to their removal. This is a newer procedure.
How Long Will It Take?
The length of a procedure depends on:
- Amount of fat to be removed
- Number of areas being suctioned
- Liposuction technique being used
How Much Will It Hurt?
Anesthesia numbs and relaxes the body. Let your doctor know if you experience pain during the procedure. Recovery from liposuction can be painful. Ask your doctor about pain relievers to help manage the pain.
Post-procedure Care
At the Care Center
- You will be taken to a recovery room for monitoring.
- IV fluids may be given to aid in hydration.
- You may be asked to take short walks to improve blood circulation.
- Pain medicine may be prescribed to help manage discomfort.
- An elastic garment to help speed recovery will be given with instructions for usage.
When five liters of fat or more is removed, an overnight stay will be required.
At Home
- Walk around as directed. This will help blood circulation and prevent blood clots from forming.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Refrain from resuming activities until directed to do so.
- Ask your doctor about when it is safe to shower, bathe, or soak in water.
- Take pain medicine as prescribed.
- Wear the elastic garment as directed.
- Refrain from smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Arrange for follow-up doctor visits.
- Be sure to follow your doctor’s instructions .
Results of the liposuction will not be seen right away. Depending on the amount of fat removed and the body’s ability to heal, visible results may take weeks or months to appear. Typically, swelling begins to decrease within a few weeks of surgery. However, it may take months to fully subside. Bruising may last three or more weeks. Numbness may persist for several weeks before it begins to fade. After the swelling and bruising disappear, the true result of the procedure is seen. If postoperative weight is maintained, the results of the liposuction can be permanent.
If desired results are not achieved, or if the skin remains loose, additional surgery may be needed.
Call Your Doctor
After arriving home, contact your doctor if any of the following occurs:
- Signs of infection, including fever and chills
- Persistent high temperature
- Oozing or discharge from incisions
- Bleeding
- Redness or increased swelling
- Increased pain or tenderness
- Coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, severe nausea, or vomiting
- Signs of shock (pale clammy skin, confusion or weakness, rapid pulse)
- Depression
In case of an emergency, call for medical help right away.
