परिभाषा
Trauma is a serious injury or shock to the body. It is caused by a physical force, such as violence or an accident. The injury may be complicated by psychiatric, behavioral, and social factors. This can cause the disability to be greater than just physical injuries. This condition almost always requires care from healthcare professionals.
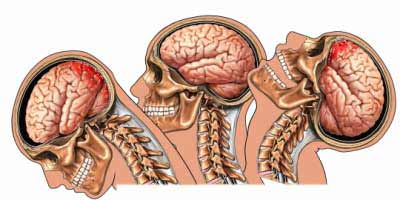
का कारण बनता है
Some causes of trauma include:
- मोटर वाहन दुर्घटनाएँ
- फॉल्स
- डूबता हुआ
- Gunshots
- Fires and burns
- Stabbing
- Other physical assault
- Fire, flood, earthquake, or other natural disaster
- Other shocking experience
जोखिम कारक
Some factors increase your chances of developing trauma. You are at increased risk if you are aged 1-44 years.
लक्षण
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, do not assume it is caused by trauma. These लक्षण उत्पन्न हो सकते हैं by other, less serious health conditions. The symptoms associated with trauma vary and depend on the type of injuries you have suffered. If you experience any of them, see your doctor.
- Multiple injuries
- Airway obstruction
- साँस लेने में समस्या
- खून बह रहा है
- दिल की धड़कन रुकना
- Lung failure
- Vital organ damage
- Central nervous system injury
- Sepsis
- Multiple organ failure
In addition, the following psychological effects may occur in response to trauma:
- Anxiety, numbness, dissociation and/or inappropriate calmness
- Anger and frustration
- Acute stress disorder (ie, distress, memories, avoidance, and numbing in the months after trauma)
- अवसाद
- Post-traumatic symptoms and/or disorder
- Avoidance and public anxiety
निदान
A medical team will assess your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done.
परीक्षण शामिल हो सकते हैं निम्नलिखित:
- Blood pressure measurement
- Ventilatory monitoring—breathing tests to determine whether breathing needs to be assisted by a ventilator or supplemental oxygen
- Electrocardiogram —to monitor heart rate
- Chest exam
- Abdomen and pelvis exam
- Exam of the extremities
- Neurologic exam
- Chest radiograph—to view the organs and structures within the test
- Abdominal ultrasound —to view the organs and structures within the abdomen
- CT scan —to view the organs and structures within the abdomen, pelvis, chest, and/or head
- Spine x-ray—to determine if there is damage to the spine
- Angiography —to identify arterial bleeding
- Other tests, depending on the nature of the injuries
- Assessment for psychological symptoms
उपचार
Talk with your doctor about the best plan for you. Treatment usually includes the following:
- Resuscitation and/or stabilization—normalize vital signs, control blood loss, and restore organ function will be restored first
- Further surgeries and/or treatments—may need further surgeries and treatments
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy —to address ongoing psychological symptoms from the trauma
रोकथाम
To help reduce your chances of trauma, the CDC and the National Safety Council recommend that you take the following steps:
- Always use seat belts.
- Never drive or operate any equipment while under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Certain medicines can be dangerous as well.
- Do not use a cell phone while driving.
- Keep poisons, medicine, and cleaning supplies locked up. Keep them away from small children.
- Teach children to swim. Teach all family members about water safety.
- Develop a fire safety plan.
- Make sure all alarm and fire equipment is up to date (eg, smoke alarms, carbon monoxide alarms, and fire extinguishers).
- If you have firearms in the house, make sure they are kept unloaded. Keep them in a locked location.
- Wear helmets while biking.
- Wear the right safety equipment for all sports and recreation activities.
- Wear appropriate protective gear when using power tools.
- Help prevent falls in the home. Install night lights, grab bars, and hand rails.
- Avoid putting yourself at risk for an accident, violence, or other physical trauma.
