Definition
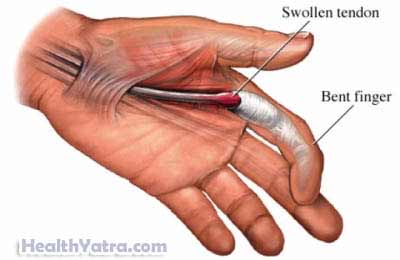
Tendons connect bones to muscles in the body. Flexor tendons of the thumb and fingers pull the fingers into a fist. The tendons are enclosed in a synovial sheath. When this sheath becomes inflammed it is called trigger finger.
Usually, tendons slide easily through the sheath as the finger moves. In the case of trigger finger, the synovial sheath is swollen. The tendon cannot move easily. This causes the finger to remain in a flexed (bent) position. In mild cases, the finger may be straightened with a pop. In severe cases, the finger becomes stuck in the bent position. Usually, this condition can easily be treated. Contact your doctor if you think you may have trigger finger.
Causes
Often, the cause of trigger finger is unknown. However, many cases of trigger finger are caused by one of the following:
- Overuse of the hand from repetitive motions:
- Computer operation
- Machine operation
- Repeated use of hand tools
- Playing musical instruments
- Inflammation caused by or associated with a disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Hypothyroidism
- Diabetes
Risk Factors
The following factors increase your chance of developing trigger finger:
- Age: 40 to 60
- History of repetitive hand motions
- Sex: female
- History of certain diseases:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Hypothyroidism
- Diabetes
Symptoms
If you experience any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to trigger finger. Some of these symptoms may be caused by other health conditions. If you experience any one of them for a period of time, see your physician.
- Finger or thumb stiffness
- Finger, thumb, or hand pain
- Swelling or a lump in the palm
- Catching or popping when straightening the finger or thumb
- Finger or thumb stuck in bent position
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. The physical exam may include:
- Asking you to move the affected finger or thumb
- Feeling the hand and fingers
For severe cases, your doctor may refer you to a hand specialist.
Treatment
Talk with your doctor about the best plan for you. The goal of treatment is to reduce swelling and pain. This will allow the tendon to move freely in the sheath. Treatment options include the following:
Rest
Stopping movement in the finger or thumb is often the best treatment for mild cases of trigger finger. A brace or splint may be used. Rest may be combined with stretching the muscle tendon.
Medications
Several medications are used to treat tenosynovitis. These include:
- Corticosteroids—given as an injection into the synovial tendon sheath to reduce swelling of the tendon sheath
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help reduce inflammation and pain:
- Ibuprofen (eg, Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (eg, Aleve, Naprosyn)
Surgery
Severe cases of trigger finger may not respond to medications. In this case, surgery may be used to release the tendon from a locked position. This surgery is usually performed on an outpatient basis. It only requires a small incision in the palm of the hand.
If you are diagnosed with trigger finger, follow your doctor’s instructions .
Prevention
Avoid overuse of your thumb and fingers. If you have a job or hobby that involves repetitive motions of the hand, you can take the following steps:
- Adjust your workspace to minimize the strain on your joints.
- Alternate activities when possible.
- Take breaks throughout the day.
