Sciatica Treatment in India
Sciatica is irritation of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve begins from the lower spine on either side. It travels deep in the pelvis to the lower buttocks. From there, it passes along the back of each upper leg and divides at the knee into branches that go to the feet.
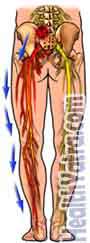
Causes
Anything that causes irritation or puts pressure on the sciatic nerve can cause sciatica, including:
- Herniated disk (or slipped disk)—the cushions between the bones of your spine bulge out of place and press on the nerve as it exits the spinal column
- Arthritis in the lower back
- Spinal stenosis —narrowing of the spinal canal in the lumbar area
- Spondylolisthesis —slippage of a bone in the lower back
- Piriformis syndrome— spasm of piriformis muscle
- In rare cases:
- Cauda equina syndrome —nerve roots at the base of the spinal cord are compressed
- Fracture in the back
- Benign or malignant tumors
- Infections
- Metabolic problems like diabetes
Risk Factors
These factors have been associated with sciatica:
- Male gender
- Obesity
- Smoking
- History of low back problems
- Anxiety and depression
- A job that requires standing for long periods of time and forward bending
- Heavy manual labor
- Heavy lifting
- Exposure to vibrations
Symptoms
Sciatica causes symptoms that can range from mild to severe.
Typical symptoms include:
- Burning, tingling, or a shooting pain down the back of one leg
- Pain in one leg or buttock may get worse with:
- Sitting
- Standing up
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Straining
- Weakness or numbness in a leg or foot
More serious symptoms associated with sciatica that may require immediate medical attention include:
- Continuing weakness in a leg or foot
- Numbness in groin or the buttocks
- Difficulty walking, standing, or moving
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Fever, unexplained weight loss, or other signs of illness
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Your doctor will pay particular attention to your back, hips, and legs. The physical exam will include tests for strength, flexibility, sensation, and reflexes.
Your doctor may need pictures of structures inside your body. This can be done with:
- X-ray
- MRI Scan
- CT Scan
Your doctor may also need to test your nerves. This can be done with a nerve conduction study.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce sciatic nerve irritation.
Treatment options include:
Stay Active
Bed rest is not generally recommended. It may only be suggested for no more than 1-2 days in those with severe pain. Your doctor may recommend that you restrict certain activities for a period of time and then resume them as soon as possible. You may be able to shorten your recovery time by staying active and exercising.
Medication
Medications used to treat sciatica include:
- Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), aspirin , or ibuprofen
- Muscle relaxers for muscle spasm
- Corticosteroid injections in the back
- Certain antidepressants or anti-seizure medications for chronic pain
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy may be done, including:
- Heat therapy
- Stretching and strengthening exercises
- Massage
- Ultrasound treatments or electrical stimulation
Alternative Therapies
These therapies have not been proven by scientific studies to have an effect on sciatica. However, some people may find some pain relief from:
- Biofeedback
- Acupuncture
Surgery
Surgery may be done to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve. This is performed in emergency situations or if other treatments fail. Common surgical procedures are microdiscectomy and lumbar laminectomy. Talk to your doctor about the right treatment plan for you.
If you are diagnosed with sciatica, follow your doctor’s instructions .
Prevention
Sciatica tends to happen more than one time. The following steps may help keep it from coming back or, in some cases, from happening in the first place:
- Lose weight. Being overweight increases the risk of sciatica as well as other back, bone, and joint problems.
- When lifting, hold the object close to your body, keep a straight back, and use your leg muscles to slowly rise.
- Practice good posture to reduce pressure on your spine.
- Begin a safe exercise program with the advice of your doctor.
- If possible, avoid sitting or standing in one position for long periods.
- Consider job retraining if your work requires a lot of heavy lifting or sitting.
- If you smoke, quit.
