Definition
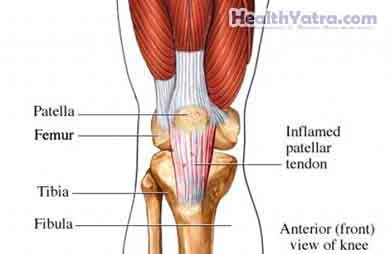
The patellar tendon connects the kneecap to the lower leg bone. Tendinopathy is an injury to the tendon. It can cause pain, swelling, and limited movement. The injury can include:
- Tendonitis—inflammation of the tendon
- Tendinosis—tiny tears in the tendon tissue with no significant inflammation
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury.
Causes
Tendinopathy is generally caused by overuse of a muscle-tendon unit. Over time, the strain on the tendon causes structural changes within the tendon.
Patellar tendinopathy occurs from overuse of the patellar tendon. Overuse may be caused by any activity that requires:
- Intense running
- Jumping
- Frequent stops and starts
- Frequent impact to the knee
- Falls
- Tendon weakness from certain diseases
Risk Factors
Factors that increase your chance of developing patellar tendonopathy include:
- Being a physically active teenager or young adult
- An increase in the frequency of training
- A sudden increase in the intensity of training
- Changing from one sport to another
- Training on a hard surface
- Repeated improper movements while training
- Muscle weakness or imbalance
- Involvement in basketball, soccer, volleyball, or running
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Pain and tenderness in the patellar tendon below the kneecap
- Pain or tightness in the knee when bending, squatting, or straightening the leg
- Discomfort in the knee when jumping, squating, or walking up stairs
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history.
Your doctor may recommend tests. Tests may include x-rays or an MRI.
Treatment
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment will depend on the severity of the injury. Options include:
Home Care
To reduce pain and swelling:
- Avoid activity that causes pain. Reduce shock or vibrations to the knee.
- Apply an ice pack for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Place a towel between the ice pack and your skin.
- Wrap your injured knee in elastic bandaging. Don’t wrap the bandage too tight. It may cut off circulation.
- Elevate your foot above your heart.
Medication
To help manage pain, your doctor may recommend:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs)
- Topical pain medications that are applied to the skin
- Prescription pain relievers
Infra-patellar Strap
This strap, also called a counterforce brace, can help support the tendon and reduce pain. It is worn as a band just below the knee.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy will help:
- Stretch and condition the quadriceps muscle, which attaches to the patella
- Maintain muscle strength, flexibility, and endurance
- Improve balance and range of motion
Cortisone Injections
If the treatments above do not reduce inflammation, your doctor may recommend that you consider a cortisone injection. Keep in mind to avoid repeated cortisone injections.
Surgery
You may need surgery if you have advanced damage to the tendon. Your doctor may also recommend surgery if you have not responded to other treatment methods over a period of several months.
Prevention
To reduce your chances of getting patellar tendinopathy, take these steps:
- Avoiding activities and sports that repeatedly stress the kneecaps, especially those that involve jumping.
- Learn proper jumping technique.
- Gradually increasing the frequency and intensity of exercise.
- Regularly doing quadriceps muscle stretching and strengthening exercises.
