Definition
Molluscum contagiosum is an infection of the skin.
Causes
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by the molluscum virus. It can start after you come in contact with the virus. You may come in contact with the virus by skin to skin contact with an infected person. The virus can also pass through shared items like towels or wrestling mats.
The virus can also spread from one part of a person’s body to another area.
Risk Factors
Skin to skin contact with an infected person is the main risk factor. Other risk factors include:
- Indirect contact with an infected person through items such as wrestling mats or by sharing towels or clothing
- Sexual contact with an infected person
- Weakened immune system (eg, HIV/AIDS)
- Having other skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis
- Living in a humid climate
Symptoms
Skin lesions are the main symptom. Similar lesions may be caused by other health conditions. It is important that you see your doctor to determine the cause.
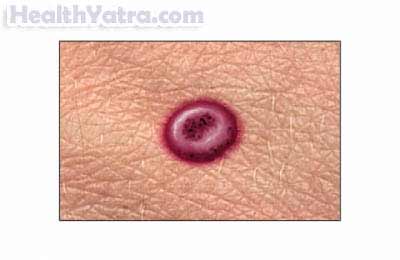
Molluscum contagiosum skin lesions usually have the following characteristics:
- Small, dome-shaped bumps with dimpling in center
- Painless, but may be itchy or tender
- Appear translucent, pearly or flesh-colored at first then may turn gray and drain
- White or waxy substance in center of lesion
- Usually multiple lesions in groups
- Face, trunk, arms, and legs are common sites in children
- Genitals, abdomen, and inner thigh are common sites in adults
- Can last from several weeks to several years
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually made based on the lesion appearance. Sometimes a biopsy will be taken. A biopsy is the removal of a small sample of the area. The sample will be looked at under a microscope.
In some cases, your doctor may refer you to a doctor that specializes in skin conditions.
Treatment
Molluscum Contagiosum usually resolves within six months to two years. For people with HIV, the lesions usually persist and spread indefinitely. Your doctor may recommend the removal of some lesions to prevent the spread of the infection or to avoid infecting others.
Treatment options include the following:
Surgical Removal
The lesions can be removed by scraping them off the surface of the skin.
Chemical Treatment
Chemicals may be used to remove the lesions. Common chemical options include:
- Salicilic acid
- Podophyllin
- Cantharidin
- Silver nitrate
- Trichloracetic acid
Cryotherapy
This method uses cold to freeze the lesions off of the skin. Liquid nitrogen may be used for this treatment.
Medical Treatment
A retinoid or imiquimod cream may be used separately or in combination. These creams gradually remove the lesions.
Prevention
This disease is very contagious. Take the following measures to reduce your risk of exposure to the virus:
- Avoid contact with an infected person. Do not share towels and clothing.
- Avoid sexual contact with an infected person..
If you have the disease, reduce the risk of spread by:
- Not touching the lesions
- Not scratching
- Washing your hands promptly if they do come in contact with the lesions
