Definition
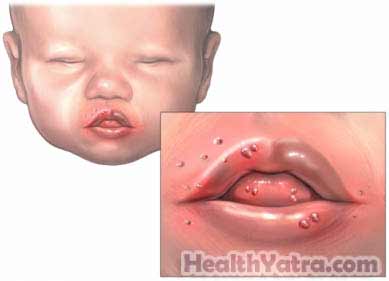
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common illness in infants and children. It is characterized by fever, sores in the mouth, and a rash on the hands and feet. It occurs in warmer months. It is transmitted primarily between humans by direct contact with secretions from the nose and throat, saliva, fluid from blisters, or the feces of those who have HFMD.
Causes
HFMD is caused by a virus from a group of viruses called enteroviruses.
Risk Factors
The following factors increase the risk of HFMD:
- Contact with someone who is infected
- Age: children under 10 years old
Symptoms
- Mild fever
- Poor appetite
- Discomfort
- Sore throat
- Painful sores in the mouth
- Skin rash that does not itch, usually on the palms of hands and soles of feet
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done.
Your doctor may need samples of bodily tissues and waste products. This can be done with:
- Throat swab
- Stool specimen
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for HFMD. Treatment is focused on relieving fever, aches, and pain associated with the illness. Medicines may be given to help relieve the pain related to the sores in the mouth.
Prevention
To help reduce the risk of HFMD:
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after diaper changes.
- Clean contaminated surfaces with soap and water followed by a diluted solution of chlorine-containing bleach. (Mix about 1/4 cup of bleach with one gallon water.)
- Avoid close contact with children with HFMD.
