Definition
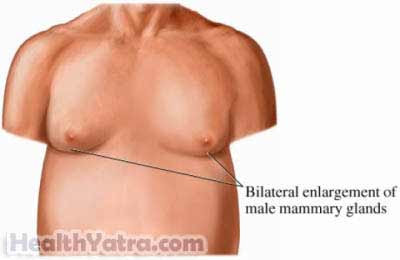
Gynecomastia is an enlargement of the breasts in men. This condition is not the same as having a fatty breast area from obesity. The breast tissue is firm in men with gynecomastia.
This may occur in up to one-third of men. About 65% of boys will develop some degree of breast enlargement during puberty. This is normal and usually goes away by age 18.
Causes
All men produce male and female hormones. Normally men produce much more male hormones than female hormones. Gynecomastia is caused by an imbalance in the female and male hormones. The hormone imbalance can be caused by:
- Adolescent puberty changes
- Aging, especially in association with low testosterone levels
- Certain genetic disorders causing low levels of testosterone
- Certain medications, such as digoxin (a heart medication), spironolactone (a diuretic), cimetidine (a medication for stomach conditions), and many others
- Anabolic steroids used to enhance athletic performance in sports
- Marijuana use
- Liver or kidney failure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland)
- Tumors of the testicles, lung, stomach, liver, kidney, or pituitary gland
Risk Factors
Factors that increase your chance of getting gynecomastia include:
- Age: adolescent or over 50
- Obesity
- Excess alcohol consumption leading to liver cirrhosis
- Chronic liver or kidney disease
- Presence of a condition or medication that decreases androgen or estrogen production
- Family history
Symptoms
Symptoms of gynecomastia include:
- Enlargement of the breasts with firm tissue, usually on both sides
- Tenderness
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. You may be referred to a doctor who specializes in hormone disorders.
Your doctor will be especially interested in other symptoms you have. You will also be asked about any medications you use. Your doctor will focus on your weight, breast exam, testicular exam, and any other signs of a hormone problem.
Other tests may be done if you have prolonged or large gynecomastia. Diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood sample—to check the function of your liver, thyroid, and kidneys, as well as other hormone levels
- Ultrasound—a test that uses sound waves to examine the breasts
- CT scan—a type of x-ray that uses a computer to make pictures of the breasts
- Biopsy—a sample of breast tissue may be removed and evaluated
Treatment
Treatment for gynecomastia is rarely needed. However, it is important to find and treat the underlying cause of the gynecomastia. If a medication is causing gynecomastia, your doctor will ask you to stop taking it or switch medication. If a tumor is causing the problem, your doctor will make a treatment plan for the tumor.
Medications may be needed to treat the gynecomastia. However, they can produce unwanted side effects. Surgery may also be used to remove breast tissue.
Prevention
Some gynecomastia may be prevented by avoiding known risk factors. This included avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, avoiding steroids, and refraining from marijuana.
