Definition
Electrical burns occur when a person is directly exposed to an electrical current. Although some electrical burns look minor on the skin, they can cause extensive internal damage, especially to the heart, muscles, or brain. This is a potentially serious condition that requires care from a doctor.
Causes
Electrical burns result from accidental contact with exposed parts of electrical appliances or wiring, such as:
- Children biting on electrical cords
- Poking utensils or other metal objects into electrical outlets or appliances, like a plugged-in toaster
- Failing to shut the power supply before making home repairs or installation
- Dropping a plugged-in appliance into water
- Occupational accidents due to, for example, electric arcs from high-voltage power lines. (Electric arcs occur when a burst of electricity jumps from one electrical conductor to another, such as flashes of electricity from the wheels of an electrically powered train or where a trolley car connects to an overhead power line.)
Risk Factors
Any exposure to an electrical current is a risk factor for electrical burns.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Visible burns on the skin
- Muscle contraction or pain
- Numbness or tingling
- Weakness
- Bone fractures
- Headache
- Feeling disoriented
- Low blood pressure
- Seizures
- Heart arrhythmias
If you experience any of these symptoms do not assume it is due to an electrical burn. These symptoms may be caused by other, less serious health conditions. If you experience any one of them, consult a doctor.
Electricity can also cause cause cardiac arrest, respiratory failure, and/or unconsciousness.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, and do a physical exam.
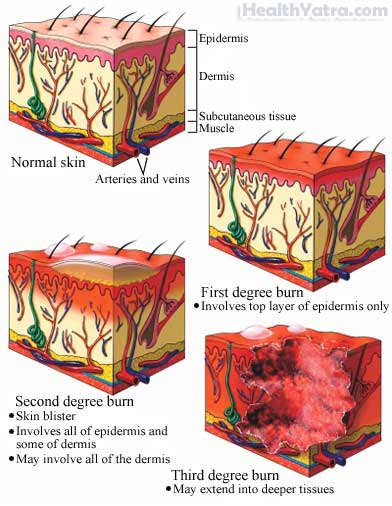
Like other burns, electrical burns have three degrees of severity, each with distinctive symptoms:
- First-degree burns —Injury is only to the outer layer of skin. They are red and painful, and may cause some swelling. The skin turns white when touched.
- Second-degree burns —These burns are deeper and more severe. They cause blisters and the skin is very red or splotchy. There may be more significant swelling.
- Third-degree burns —These cause damage to all layers of the skin down to the tissue underneath. The burned skin looks white or charred. These burns may cause little or no pain because the nerves in the skin are destroyed.
It may be more difficult to diagnosis damage under the skin cuased by electricity. Test may include:
- Electrocardiogram —to detect rhythm disturbances of the heart
- Urine or blood tests—to check for severe damage to muscles
Treatment
Electrical burns require an immediate call to paramedics. If possible, shut off the electrical current from its source (such as unplugging a cord or turning off the circuit breaker). Often, simply turning off the appliance itself will not stop the flow of electricity.
If the current can’t be turned off, use a non-conducting object, like a wooden broom, chair, rug, or rubber doormat to push the victim away from the source of the current. Don’t use a wet or metal object. If possible, stand on something dry and non-conducting, such as a mat or folded newspapers.
Do not attempt to rescue a victim near active high-voltage lines.
Once the victim is free from the source of electricity, his airway, breathing, and pulse are checked and, if needed, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) efforts are started. The victim is covered with a blanket to maintain body heat and feet are raised above the head.
Ice, butter, or ointments, should not be applied.
Anyone with an electrical burn should be taken to the hospital for further evaluation. Treatment will depend on the severity of the burn and any other associated complications.
If you are diagnosed with an electrical burn, follow your doctor’s instructions .
Prevention
To help reduce your chances of an electric burn, take the following steps:
- Use child safety plugs in all outlets.
- Keep electrical cords out of children’s reach.
- Avoid electrical hazards by following manufacturer’s safety instructions when using electrical appliances. Always turn off circuit breakers before making repairs to wiring.
- Avoid using electrical appliances while showering or wet.
- Never touch electrical appliances while touching faucets or cold water pipes.
Keywords :
Electrical Burns Definition, Electrical Burns Causes, Electrical Burns Symptoms, Electrical Burns Complications, Electrical Burns Surgery Cost in India, Electrical Burns Treatment Hospital in India, Electrical Burns Treatment in India, Electrical Burns Doctors in India, Electrical Burns Meaning in Hindi, Electrical Burns Meaning in Bengali, Electrical Burns Meaning in Arabic, Electrical Burns Treatment cost in 2024, Electrical Burns Hospital in India, Electrical Burns Treatment Near Me, electric burn treatment, management of electrical burns pdf, types of electrical burns, electrical burns ppt, high-voltage electrical burns, how to treat electrical burns on fingers, electrical burns signs and symptoms
