Definition
A contusion occurs when blood vessels are damaged or broken after an injury. The raised area of the contusion is the result of blood and fluid leaking from the injured blood vessels into the tissue. You usually see a discolored, purplish area that takes 2-3 weeks to go away.
The condition is a minor problem that usually needs little treatment. Consult with your doctor if the injury does not clear up within a few weeks or if it is severe.
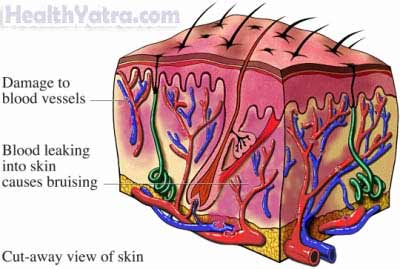
Causes
Contusions are caused by minor accidents to your skin, such as falling, bumping into something, or being hit or kicked.
Risk Factors
Almost everyone suffers contusions as a result of routine bumps. People who are at higher risk include:
- Children and teens
- People who play contact sports
- People with blood-clotting problems
- People taking blood-thinning medicine (eg, coumadin, aspirin)
Symptoms
Symptoms of minor contusions usually include:
- Skin discoloration (usually blue and/or purple, fading to yellow)
- Pain
- Swelling
Diagnosis
The skin discoloration, pain, and swelling of a contusion are enough to diagnose the condition.
Treatment
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment options to help lessen the swelling and pain include:
- Applying ice or a cold pack to the injured are (Do not place ice directly on your skin.)
- Elevating the injured area above the level of your heart
- Taking pain relieving medicine if recommended by your doctor
You may need addition treatment from your doctor if you:
- Have a more serious injury (eg, fracture)
- Have broken the skin (may need a tetanus shot or antibiotics)
If you are diagnosed with a contusion, follow your doctor’s instructions .
Prevention
Using proper safety equipment can help prevent contusions.
