Definition
Syphilis is an infection caused by bacteria. Congenital syphilis is an infection that a baby is born with. In this case, the infection is passed from a mother to her baby.
This is a potentially serious condition that requires care from your doctor. If untreated, a baby with congenital syphilis can have problems throughout life. It can also cause a stillbirth or death in early infancy.
Causes
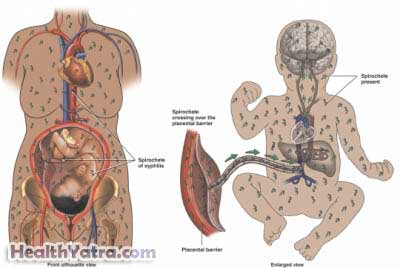
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease. It is caused by the bacteria calledTreponema pallidum. This infection can pass to a baby through an infected mother. The baby may be infected during pregnancy or the birth process.
Risk Factors
A baby has an increased risk of developing congenital syphilis if the mother:
- Does not receive prenatal care
- Abuses drugs before or during pregnancy
- Is involved in prostitution
- Has unprotected sex
Symptoms
If your baby has any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to congenital syphilis. These symptoms may be caused by other health conditions. Potential symptoms include:
- Rash around the mouth, anus, genitals
- Poor weight gain (failure to thrive)
- Difficulty feeding
- Fever
- Severe pneumonia
- Deformities of the nose, upper arm, shins
- Tooth abnormalities
- Neurological problems
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Irritability
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam may be done. Tests may include the following:
- Blood tests of the mother and the baby to identify the presence of syphilis
- Tests on the placenta
- Spinal tap to look for the presence of syphilis in the spinal fluid
- Eye exam
- Bone x-rays
Treatment
Syphilis is treated with an antibiotic called penicillin. It may be given to the mother during pregnancy. The medicine in pregnancy will treat the child as well the mother. Penicillin will also be given to infected babies after birth.
Other steps may be needed if your child has complications from syphilis. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you.
Prevention
To help reduce your chances of passing on congenital syphilis, take the following steps:
- Practice safer sex.
- If you become pregnant, get good prenatal care throughout pregnancy.
- If you think you may have a sexually transmitted disease, get tested. Follow through on all your doctor’s recommendations.
- Take your baby to all newborn and well-child checks. Follow your doctors recommendations for screening tests and immunizations.
