Definition
A coma is a state of deep unconsciousness that a person cannot be woken from. A person in a coma cannot react to events in the environment.
Causes
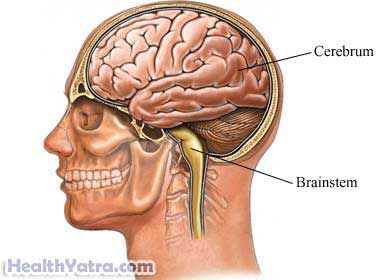
Information about your environment is normally passed from the brainstem into the rest of the brain. This feedback allows a person to be aware of and react to the environment. A coma is caused by a breakdown in this system.
The system may be interrupted by:
- Severe head injury—most often a results of car accidents, violence, or falls.
- Brain illness such as:
- Brain tumor
- Brain hemorrhage or stroke
- Brain infection
- Lack of oxygen to the brain which may be due to:
- Very high blood pressure
- Very low blood pressure or shock
- Cardiac arrest
- Severe seizures
- Severe general illness such as:
- Severe bodily infections
- Severe acute liver or kidney failure
- High carbon dioxide levels
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Toxicity from poisons, medication, alcohol, or drugs
- Abnormal hormone levels, such as from the thyroid or adrenal gland
- Abnormal blood chemistries, such as sodium or calcium
- Very low or very high levels of blood sugar
- Very low or very high body temperatures
- Severe nutrient deficiency
- Liver failure
- Kidney failure
- Inherited metabolic diseases
Risk Factors
Risk factors for coma include:
- Severe illness
- Diabetes
- Liver, kidney, or cardiovascular disease
- Tendency to have blood clots
- Exposure to poisonous substances (eg, carbon dioxide)
- Cancer and chemotherapy
Risk factors for brain injury include:
- Age: 5 years or younger, 15-24 years old, and 75 years or older
- Sex: male
- Traveling in a vehicle at a high rate of speed or at night
- Lack of sleep
- A previous head injury
Symptoms
Symptoms of a coma include the following:
- No response to stimulus, such as:
- Pain
- Sound
- Touch
- Sight
- Spontaneous body movements, such as:
- Jerking
- Shaking
- Trembling
- Eyes opening and closing
- Irregular breathing
Diagnosis
Since the patient cannot speak, the doctor will need to gather information from other sources. The doctor may need to speak to friends, family members, and people who witnessed the accident. This is important to help with diagnosis. The doctor will also need to know about the person’s medical history and any drug or alcohol use. It is important to provide honest information in order to help with treatment.
The doctor will test reflexes, listen to breathing, and examine the eyes. A physical exam will also be done including tests of the nervous system. In addition, the following tests may be done:
- Blood tests—to check blood glucose levels, organ function and screen for infection and toxic substances
- Urine test—to test for the presence of drugs
- Imaging tests, such as:
- Neck x-rays —in cases where head and neck trauma may have occurred, a test that uses radiation to take pictures of structures inside the body
- MRI scan —a test that uses magnetic and radio waves to make pictures of the inside of the body, in this case the brain
- CT scan —a type of x-ray that uses a computer to make pictures of the inside of the head
- SPECT or Xenon—enhanced CT scan to test for blood flow and metabolic activity within the brain
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) —a test that records the brain’s activity by measuring electrical currents through the brain
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture) —removal of a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid to check for pressure, blood, and infection
- Evoked potentials—a test for brain wave activity after stimulation of the sensory nerves (including the auditory nerves) of the body
Clinical findings of comatose patients can be rated according to the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). This scale assesses three different functions: eye opening, motor response, and verbal response. Scores can range from 15 to 3. A lower score indicates less responsiveness. Scores are interpreted as follows:
- 15-13—mild brain injury
- 12-9—moderate brain injury
- 8 or less—a severe brain injury
Treatment
A coma is a medical emergency. Any unconscious person should be taken to the emergency room immediately.
Emergency Treatment
Doctors will work quickly to determine the cause of the coma. Further treatment will depend on the cause of the coma. Supportive care may include:
- Monitoring of vital signs
- Oxygen therapy
- Delivering fluids directly into the blood through an IV
- Ventilator to help support breathing
If a specific cause of the coma is suspected, supportive care may also include:
- Glucose delivered through IV—in case low blood sugar is causing the coma
- Naloxone—if a narcotics overdose is suspected
- Thiamine (vitamin B1) may be given with glucose if alcoholism or malnutrition is suspected
In some cases, surgery may correct the cause of a coma.
Ongoing Treatment
If the coma persists after emergency care, ongoing care may be needed. Once the person is stabilized, treatment will focus on providing nutrition and preventing infections. The care staff will also work to prevent bed sores.
Prevention
The following can help decrease your risk of coma:
- Wear a seatbelt. Make sure infants and small children are securely fastened in a child safety seat.
- Children aged 12 years and under should ride in the back seat of a vehicle.
- Wear an appropriate helmet while biking, rollerblading, playing contact sports, skiing, snowboarding, and riding a motorcycle.
- Wear athletic mouth guards while playing sports.
- Don’t abuse alcohol or drugs.
- If you have diabetes, see your doctor regularly and take appropriate steps to regulate your blood sugar levels.
- If you are ill or take medicine, see your doctor regularly for check-ups.
Coma Treatment in India
Coma Treatment in India has seen remarkable advancements and holistic approaches with the aid of HealthYatra’s medical consultation service. When a patient experiences a coma, time is of the essence, and early intervention is crucial. HealthYatra’s platform connects patients and their families to a network of highly skilled and experienced medical professionals across India, facilitating prompt diagnosis and effective treatment plans. Through HealthYatra, patients gain access to state-of-the-art medical facilities equipped with advanced diagnostic tools, critical care units, and neurological interventions. Moreover, the platform emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach, combining critical care management, neurological interventions, and personalized rehabilitation programs to maximize the chances of patient recovery. HealthYatra’s commitment to providing comprehensive and compassionate care plays a pivotal role in enhancing the outcomes of coma treatment in India, providing hope and support to patients and their families during challenging times.