Definition
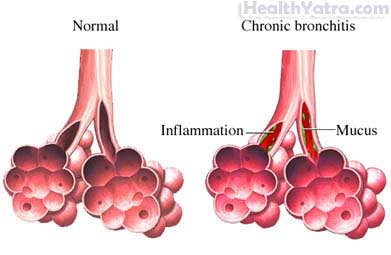
Chronic bronchitis is a long term disease of the lungs. It is a problem with the airways of the lungs. Injury or irritation causes these airways to swell and develop extra mucus. This makes it difficult to move air in and out of the lungs. It will make breathing difficult.
Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Causes
Chronic bronchitis is caused damage to the airways. The damage is caused by:
- Cigarette smoking
- Inhaling toxins or other irritants
- Genetic predisposition can make a person’s lungs more susceptible to damage from smoke or pollutants (alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency)
Risk Factors
Cigarette smoking is the greatest risk factor for developing chronic bronchitis. The more you smoke and the longer you smoke, the greater your chance of developing chronic bronchitis. Frequent and long-term smoking also increases the chance of severe chronic bronchitis.
Chronic bronchitis is more common in people over 40 years old. Other factors that may increase your risk of chronic bronchitis include:
- Long-term exposure to chemicals, dust, and other substances that have been inhaled
- Long-term cigar or marijuana smoking
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Family members with COPD
- History of frequent childhood lung infections
- Long term asthma
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Cough
- Increased mucus production
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, especially after mild activity or exercise
- Recurring respiratory infections that cause symptoms to worsen
- Wheezing when breathing
- Fatigue
Diagnosis
To diagnose chronic bronchitis, symptoms of productive cough must have been present for three or more months in at least two consecutive years, and not have been caused by another condition. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Tests may include the following:
- Breathing tests to check lung function
- Blood tests including
- Complete blood count
- Arterial blood gas tests
Images of the lungs may be taken with:
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the chest
Treatment
. There is no cure for chronic bronchitis. There are treatments that can reduce symptoms and improve lung function. The best way to reduce symptoms is to stop smoking.
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Options may include one or more of the following::
Medication
Medications may include bronchodilators or steroids. They may help manage chronic bronchitis by:
- Opening the airways
- Relaxing the breathing passages
- Decreasing inflammation
Some medication may be taken as pills or liquids. Others are inhaled medication that is delivered directly to the lungs.
Antibiotics are rarely prescribed to treat chronic bronchitis. They may be needed to treat a lung infection that has developed because of the chronic bronchitis.
Vaccines
The flu and pneumonia can make your symptoms worse. Get vaccinated againstpneumonia and the flu. The flu vaccine may also reduce flare-ups.
Oxygen
Oxygen therapy may be helpful if the oxygen levels in your blood are too low. It can relieve trouble breathing and improve energy. You may only need it for specific activities or it may be given throughout the day.
Exercise
Special exercises can strengthen chest muscles. This can make it easier to breathe.
Regular physical activity can reduce the workload on your lungs by building your endurance. Physical activity is also associated with improved quality of life. Follow your doctor’s recommendations for activity levels and restrictions.
Breathing and Coughing Techniques
Special methods of breathing can help bring more air into the lungs. It can also help force trapped air out of the lungs. Effective coughing techniques can also help clear mucus from your lungs. Ask your doctor if these techniques can help you. Some examples include:
- Pursed lip breathing
- Controlled coughing technique
Lifestyle Changes
The following may help you manage your symptoms:
- Pace your activities.
- Learn relaxation techniques and other methods to manage stress.
- Seek emotional support from professionals, family, and friends. Anxiety can increase the rate of respiration, making breathing more strenuous.
Prevention
To reduce your chances of getting chronic bronchitis, take these steps:
- If you smoke, quit.
- Avoid exposure to second-hand smoke.
- Avoid exposure to air pollution or irritants.
- Wear protective gear if exposed to irritants or toxins at work.

