Definition
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in the United States.
Treatment includes antibiotics, partner notification, and lifestyle changes.
Causes
Chlamydia is caused by a bacterium that is transmitted from an infected partner during sex. This can happen during oral, vaginal, or anal sex.
Risk Factors
Chlamydia is most common among sexually active teens and young adults. Other factors that increase your chances of getting chlamydia include:
- Being sexually active
- Multiple sexual partners
- Having sex without a condom
- History of STDs
Symptoms
Most people who have chlamydia do not have symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they might appear within 1-3 weeks of exposure.
Symptoms in men may include:
- Purulent discharge from the penis
- Burning, itchy, or painful sensation while urinating
Symptoms in women may include:
- Increased or abnormal vaginal discharge
- Vaginal redness or irritation
- Painful and frequent urination
- Unusual vaginal bleeding, or bleeding between periods
- Pain or bleeding during or after sex
- Abdominal pain
Pregnant women can transmit chlamydia to their newborns during birth. This may cause conjunctivitis or pneumonia in the baby. Identification and treatment during pregnancy can greatly reduce risks for the baby.
Chlamydia can also cause serious health complications.
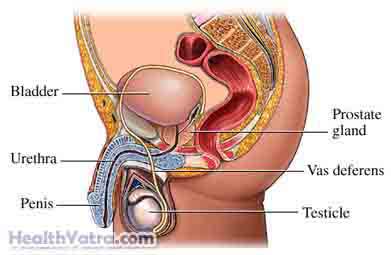
Complications in men include:
- Epididymitis—A painful swelling and inflammation of the testicles, which may lead to infertility.
- Urethritis—The inside of the urethra may become inflamed, which causes burning when passing urine. If scarring occurs, it may cause difficulty with passing urine, or block urine flow completely.
- Prostatitis—An inflammation of the prostate gland. Symptoms include pain in and around the groin and pelvis, or discomfort when urinating. It may also create flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, body aches, or fatigue.
- Reiter’s syndrome—A triad of urethritis, arthritis, and conjunctivitis.
Complications in women include:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)—A serious infection that can lead to infertility, even in women who never have symptoms. If symptoms do occur, they may include pelvic pain and pain with intercourse. PID causes scar tissue, or may cause an abscess to form, in the fallopian tubes.
- Tubal pregnancy—Scarring in the fallopian tube also increases the risk of a tubal pregnancy and infertility. A tubal pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg cannot reach the uterus. It is a serious condition that may cause a rupture, bleeding, or infection inside the abdomen. A ruptured or bleeding tubal pregnancy is considered a surgical emergency.
- Abdominal inflammation—Chlamydia and gonorrhea may cause inflammation around the reproductive organs, the appendix, or the liver. When the liver is involved, symptoms resemble gallbladder disease, with fever and pain under the right ribs. This condition is called Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. Diagnosis is based on tests.
Tests may include:
- A swab from the penis, cervix, throat, or rectum to test the discharge.
- Urine test.
- Other STD tests, such as gonorrhea, syphilis, or HIV.
Treatment
Chlamydia is treated with antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics are:
- Azithromycin
- Doxycycline
To ensure successful treatment:
- It is important that you and your partner both be treated. Wait at least seven days before you have sex again.
- If you still have symptoms after the medication is finished, or if you are pregnant, you may need to be tested again.
- You should be tested again three months after treatment to make sure you have not been reinfected.
If you are diagnosed with chlamydia, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Prevention
To reduce the chances of getting chlamydia, take these steps:
- Always use a latex condom during sexual activity.
- Have routine check-ups for STDs if you are under the age of 25.
- Have check-ups often if you have other risk factors for getting STDs.
- Have a monogamous relationship. Monogamous means only one sexual partner.
