Definition
Central cord syndrome (CCS) is a type of incomplete spinal cord injury. CCS is marked by damage to the nerve fibers that bring messages from the brain to the body. This condition affects how you can use your arms and hands, and in some cases, your legs. There may be a loss of sensation and motor control.
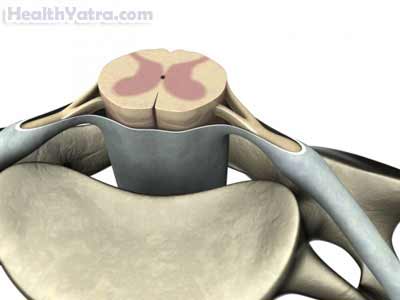
Causes
CCS is caused by damage to the central part of the spinal cord. This damage may occur when the neck is hyperextended. This can can be associated with:
- Syringomyelia (syrinx)—a cyst in the spinal cord
- Loss of blood supply to the area
- Bleeding in the spinal cord
- Swelling
Common causes of injury include:
- Trauma (eg, car accident, sports injuries, falls)
- Degenerative condition of spine (often found in older people)
- Pre-existing condition, such as being born with a narrow spine
CSS can also be due to:
- Structural problems
- Tumors within the spinal cord
Risk Factors
Males over 50 are more likely to have this condition. Risk factors that increase your chances of developing CCS include:
- Autoimmune disorder (eg, multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica)
- Pre-existing condition (eg, narrow spinal canal, spinal cord disease, tethered cord)
- Participation in certain sports (eg, wrestling, diving)
Symptoms
If you have any of these symptoms, do not assume it is due to CCS. These symptoms may be caused by other conditions.
- Unable to lift arms and hands completely, or numbness and tingling
- Difficulty with fine motor control (eg, buttoning a shirt)
- Muscle weakness in legs, difficulty walking
- Loss of bladder control
If CCS is due to trauma, symptoms usually come quickly. Sometimes, however, symptoms may come more slowly.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. A neurologic exam may also be done.
Your doctor may want pictures of your spinal cord. These can be taken with:
- MRI scan
- CT scan
- Myelogram
- X-ray
Treatment
Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Rehab can take a long time for some patients. If you are young and have more muscle function, you have a better chance of recovering.
Treatment options include the following:
Nonsurgical Treatment
In most cases, surgery is not needed. Often treatment involves:
- Restricting neck movement
- Giving steroids
- Doing physical and occupational therapy
Surgery
Surgery is needed if there is a large compression of the spinal cord fibers. Surgery may also be done after a period of recovery. For example, if you still have cord compression after a recovery period.
Prevention
To help reduce your chance of getting a spinal cord injury, take the following steps:
- Avoid diving if you do not know how deep the water is.
- Always wear a seatbelt.
- Do not drink and drive. Do not ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Remove obstacles in your house, like throw rugs, that could cause falls.
- Use safe methods and proper equipment when playing sports.
- Secure firearms.
