Definition
Hard calcium deposit can form on soft tissue, in this case tendons. Once the calcium deposits are formed, the tendons may become inflamed and cause pain. This inflammation and pain is called calcific tendonitis. This condition usually develops over time. Symptoms typically do not appear until after the calcium has formed. Shoulder pain develops once the calcium deposit begins to be reabsorbed by the body.
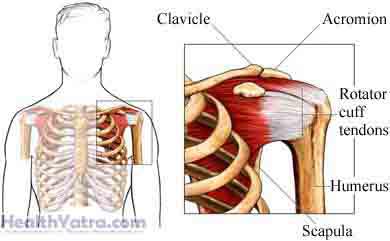
This condition may be treatable. If you suspect you have this condition, contact your doctor.
Causes
The exact cause is unknown. The condition occurs most commonly from wear and tear of the shoulder. Aging also plays a part in its development. It is more common among people over age 40.
Risk Factors
These factors increase your chance of calcific tendonitis. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
- Over age 40
- Female
Symptoms
If you have any of these symptoms do not assume it is due to calcific tendonitis. These may be caused by other conditions. Tell your doctor if you have any of these:
- Sudden onset of pain
- Intense pain with shoulder movement
- Stiffness of shoulder
- Loss of shoulder range of motion
- Pain that disrupts sleep
- Tenderness over rotator cuff
- Loss of muscle
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. You may be referred to a specialist. For example, an orthopedic surgeon specializes in bones.
Tests may include the following:
- Thorough physical evaluation—assessing your shoulder range of motion and stability
- X-ray —test that uses radiation waves to form a picture of the body’s structures; used to view calcium deposit(s)
Treatment
Most cases of calcific tendonitis resolve over time. Talk with your doctor about the best plan for you. Options include the following:
Medical Treatment
Your medical treatment plan will likely include:
- Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Rest
- Heat and/or ice
- Physical therapy to strengthen muscles
- A steroid (such as cortisone) shot directly into your shoulder—might be used to decrease inflammation and pain
Physical Therapy
Your doctor may send you to a therapist for treatment. A therapist will use different treatments to decrease the pain and inflammation. Possible treatments include:
- Ice
- Heat
- Ultrasound—a device that uses high energy sound waves to decrease pain in soft tissue
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)—used to decrease muscle stiffness or spasms
Once the symptoms have started to decrease, you will work with the therapist to strengthen your muscles and increase your range of motion.
Lavage Treatment
Lavage may help flush out the calcium deposits. A needle is placed directly into the shoulder. Normal saline is injected through the needles. The deposits are then broken up for removal.
Shock Wave Therapy
This therapy breaks up deposits by sending sound waves to the shoulder. The body can then reabsorb the smaller pieces. This should decrease symptoms.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be done to remove deposits. The procedure is calledarthroscopy. It uses small incisions and instruments to view the joint and remove the deposits.
Prevention
There are no known ways to prevent this condition.
