Definition
Arrhythmias are abnormal beats of the heart. Types of arrhythmias include:
- Heartbeats that are too slow (bradycardia)
- Heartbeats that are too fast (tachycardia)
- Extra beats
- Skipped beats
- Beats coming from abnormal areas of the heart
Causes
An arrhythmia can be caused by:
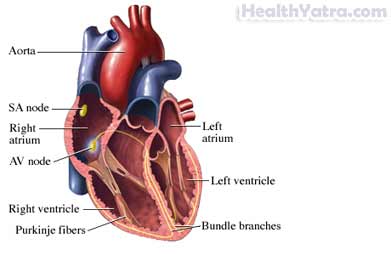
- The heart’s natural pacemaker (sinoatrial node [SA node]) developing an abnormal rate or rhythm
- The normal conduction path being interrupted
- Another part of the heart taking over as pacemaker
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of arrhythmias include:
- Lifestyle factors, such as excess caffeine, stress, smoking, alcohol abuse, drug abuse (eg, cocaine abuse)
- Certain medicines, such as diet pills, decongestants, and antidepressants
- Heart-related conditions, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), problems with heart valves, heart muscle damage after heart attack, rheumatic heart disease,cardiomyopathy
- Other conditions, such as anemia, high blood pressure, diabetes, liver disease, endocrine disorders (eg, thyroid or adrenal gland problems), typhoid fever,hypothermia, electric shock or lightening strike, near-drowning
Symptoms
Some arrhythmias may occur without any symptoms. Others may cause noticeable symptoms, such as:
- Fainting
- Dizziness, sensation of light-headedness
- Sensation of your heart fluttering (palpitations)
- Sensation of a missed or extra heart beat
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. The doctor will listen to your heart with an instrument called a stethoscope.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests and urine tests
- Your doctor may need pictures of your heart. This can be done with:
- Echocardiogram
- Nuclear scanning
- Coronary angiography
- Your doctor may need to record your heart functions. This can be done with:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)—records the heart’s activity by measuring electrical currents through the heart muscle
- 24-hour Holter monitor (a portable EKG that you wear as you do your daily activities)
- Exercise stress test—ecords the heart’s electrical activity during increased physical activity
- Electrophysiological study—shows electrical impulses as they travel through the heart
Treatment
Treatment may include:
- Anti-arrhythmic medicines—These will help slow down or speed up your heart rate, or return your heart rhythm to normal.
- Cardioversion—These treatments involve placing paddles on the chest or back. An electrical current is passed through the chest wall to the heart. The current resets the heart’s electrical circuits. It also tries to return the heart rhythm to normal.
- Automatic implantable defibrillator—A tiny defibrillator can be surgically implanted in your chest to monitor your heart rhythm. The device will automatically shock the heart if a dangerous arrhythmia happens. This may help return the heart rhythm to normal.
- Artificial pacemaker—The pacemaker is surgically implanted in your chest. It takes over the job of providing the electrical impulses needed to have a good heart rhythm.
- Ablation—An area of the heart that is responsible for an abnormal rhythm may be surgically removed or altered (ablated) with different techniques.
- Maze procedure and mini-maze procedure—The Maze procedure creates a pattern of scar tissue in the upper chambers of the heart. This makes a pathway for electrical impulses to travel through the heart. It also blocks the pathway for fast or irregular impulses. The Maze procedure may also be done as minimally invasive surgery (called mini-Maze).
If you are diagnosed with an arrhythmia, follow your doctor’s instructions.
Prevention
To help prevent arrhythmias:
- Treat underlying conditions that might lead to arrhythmias.
- Avoid substances (eg, caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and certain medicines) that trigger arrhythmia or make it worse.
- Follow general advice to prevent heart disease, including:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Talk to your doctor about a safe exercise program.
- Do not smoke. If you smoke, quit.
- Eat a healthy diet that is low in saturated fat and rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- If you have a long-lasting medical condition, get proper treatment.
- Ask your doctor if you should take cholesterol-lowering medicine.
Arrhythmias Treatment in India – Page Keywords:
Arrhythmias Definition, Arrhythmias Definition Causes, Arrhythmias Symptoms, Arrhythmias Treatment in India, Arrhythmias Treatment Cost in India, Arrhythmias Surgery Cost, Top Arrhythmias Treatment Hospital, Top Arrhythmias Treatment Doctor in India, Arrhythmias Meaning in Marathi, Arrhythmias Treatment Near me, Arrhythmias Complications, Travel India for Arrhythmias Treatment, Arrhythmias Treatment in Arab Countries, Arrhythmias Treatment in Bangladesh, Arrhythmias Treatment in Dhaka, Arrhythmias Meaning in Bengali, Arrhythmias Meaning in Arabic, Arrhythmias Meaning in Hindi, Arrhythmias Treatment in Bahrain, Arrhythmias Treatment in Egypt, Arrhythmias Treatment in Iraq, Arrhythmias Treatment in Jordan, Arrhythmias Treatment in Kuwait, Arrhythmias Treatment in Lebanon, Arrhythmias Treatment in Saudi Arabia, Arrhythmias Treatment in United Arab Emirates, Arrhythmias Treatment in Sudan, Arrhythmias Treatment in Tunisia, Arrhythmias Treatment in Nepal, Arrhythmias Treatment cost,
