Definition
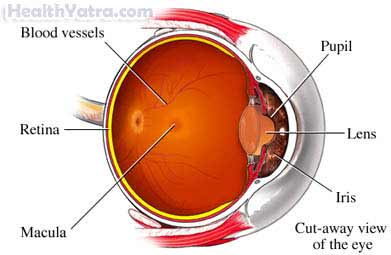
The retina is the tissue that lines the back of the eye. It sends visual signals to the brain. The macula is part of the retina. It is responsible for central vision. Macular degeneration is decline of the macula. It causes a gradual loss of sharp, central vision. The condition is mainly a disease of aging. In rare cases, it can occur in younger people.
There are two types of adult (or age-related) macular degeneration (AMD):
- Dry AMD—This occurs when an area of the retina becomes diseased. This leads to a slow breakdown of cells in the macula. The central vision is gradually lost. Dry AMD accounts for the majority of cases.
- Wet AMD—As dry AMD worsens, new blood vessels may begin to grow. These new blood vessels often leak blood and fluid under the macula. This can lead to permanent damage of the macular region. Wet AMD is very uncommon. But, it accounts for the majority of blindness from this disease.
Causes
The cause of AMD is not known.
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase your risk for AMD include:
- Age: risk increases with age, and is most commonly seen in senior citizens
- Family members with AMD
- Race: White
- Smoking
- Excessive exposure to sunlight
- Sex: women might have increased risk
- Cardiovascular risks: high blood pressure, high cholesterol
Symptoms
In some people, AMD advances very slowly. It has little effect on their vision. In others, the disease progresses faster. It may lead to significant vision loss. Neither dry AMD nor wet AMD causes pain.
Symptoms include:
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty seeing details in front of you, such as faces or words in a book
- Blurred vision that goes away in brighter light
- A small, but growing blind spot in the middle of your field of vision
- Straight lines (such as door frames) appear crooked or distorted
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical exam will be done. The doctor may suspect AMD if you are older and have had recent changes in your central vision. A specialist will look for signs of the disease. The doctor will use eye drops to dilate (enlarge) your pupils. This will allow a view of the back of the eye.
You may also be asked to view an Amsler grid. This is a pattern that looks like a checkerboard. Changes in your central vision will cause the grid to appear distorted. This is a sign of AMD.
Treatment
Treatment may include:
Dry AMD
Research has suggested certain high-dose vitamins and minerals may slow the progression of the disease in some people.
Wet AMD
Laser Photocoagulation
This procedure is used in some cases of wet AMD. A strong laser light beam is aimed at the new blood vessels. The beam destroys the vessels. It usually takes less than 30 minutes to complete. You may need more laser treatments. This treatment is used less often since the development of newer treatments.
Photodynamic Therapy
This procedure is a type of treatment that involves injecting a light-sensitive dye into your blood. The affected areas in the back of the eye are then hit with a special laser light. The light activates the dye to destroy certain blood vessels. It also takes less than 30 minutes. You may need to have additional treatments.
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor
Another way to treat wet AMD is an injection of a special medicine. It is called a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor. The medicine is injected into the vitreous (fluid) in the back of the eye. This method is growing quickly in popularity. It usually needs to be repeated multiple times. About 1/3 of patients show significant improvement in vision.
Prevention
There are no guidelines for preventing AMD. For overall eye health:
- Have regular eye exams. The exams should include dilation to closely look at the retina.
- If you smoke, quit.
- Eat a healthy diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Consider omega-3 fatty acid supplements.
If you have AMD, your doctor may advise you to use an Amsler grid at home. This will help you monitor for problems. Your ophthalmologist should discuss the various treatment options with you.
Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in India – Page Keywords:
Adult Macular Degeneration Definition, Adult Macular Degeneration Definition Causes, Adult Macular Degeneration Symptoms, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in India, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment Cost in India, Adult Macular Degeneration Surgery Cost, Top Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment Hospital, Top Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment Doctor in India, Adult Macular Degeneration Meaning in Marathi, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment Near me, Adult Macular Degeneration Complications, Travel India for Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Arab Countries, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Bangladesh, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Dhaka, Adult Macular Degeneration Meaning in Bengali, Adult Macular Degeneration Meaning in Arabic, Adult Macular Degeneration Meaning in Hindi, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Bahrain, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Egypt, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Iraq, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Jordan, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Kuwait, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Lebanon, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Saudi Arabia, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in United Arab Emirates, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Sudan, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Tunisia, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment in Nepal, Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment cost,
Adult Macular Degeneration Treatment Cost in India, Adult Macular Degeneration Top Doctors Best Hospital in India
